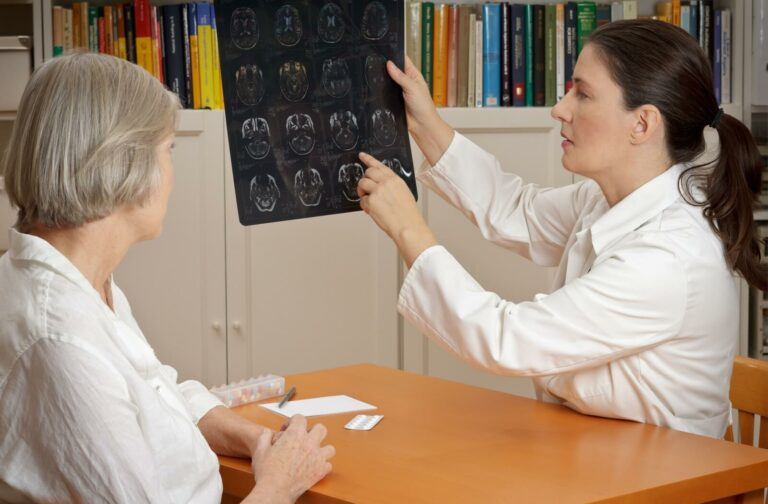
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that significantly impacts brain functions, leading to cognitive decline, memory loss, and changes in behavior.
At the center of this condition lies its impact on the brain, a complex organ responsible for our thoughts, memories, emotions, and the very essence of who we are. As Alzheimer’s develops in an individual, it leaves a trail of biological changes that not only illuminate the nature of the disease but also offer insights into the broader mysteries of the human brain.
It is a condition that affects not only the individuals diagnosed but also their families and caregivers. It is imperative to understand how Alzheimer’s impacts an individual’s brain on a neural level so we can better appreciate the challenges faced by those affected and underscore the support individuals need. The main areas of the brain that are affected by Alzheimer’s disease are:
- The hippocampus
- The amygdala
- The cerebral cortex
- The entorhinal cortex
- The basal forebrain
how is the brain affected by alzheimer’s?
Alzheimer’s typically damages the connections among neurons in the brain that deal with memory first and later in areas responsible for language, reasoning, and social behavior. Eventually, the damage spreads to surrounding neurons and will stop functioning in a typical fashion. A person with Alzheimer’s will likely gradually lose the ability to function independently, and in later stages, it can be life-threatening.
The Hippocampus
The hippocampus is crucial for forming new memories and spatial navigation. In the early stages of Alzheimer’s, the hippocampus is one of the first regions to be damaged, leading to the initial symptoms of memory loss and disorientation. The damage in this area significantly impacts an individual’s ability to form new memories and recall recent events.
The Amygdala
The amygdala plays a key role in emotional regulation and processing. Alzheimer’s can alter emotional responses and lead to unexpected mood swings or changes in personality. Damage in this area can potentially contribute to emotional disturbances such as increased agitation, anxiety, and depression. The amygdala is closely connected to other cognitive functions and may impact memory processes and social cognition.
The Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex is the brain’s outer layer responsible for critical thinking, planning, and understanding information. This includes functions such as thought, memory, awareness, and language. As Alzheimer’s progresses, the cerebral cortex shrinks significantly, affecting cognitive abilities and leading to difficulties in speaking, comprehending, and performing complex tasks.
The frontal and temporal lobes are particularly affected, contributing to the cognitive decline and personality changes observed in Alzheimer’s patients. This results in individuals having challenges performing complex tasks, understanding language, recognizing familiar faces, and conducting daily activities.
The Entorhinal Cortex
This area of the brain is vital for memory and navigation. Damage to the entorhinal cortex can result in the loss of both recent and past memories and spatial disorientation. Damage in this area underpins some of the most challenging aspects of Alzheimer’s, where it can significantly impact an individual’s sense of independence and identity.
The Basal Forebrain
This region is important specifically in cognitive functions such as attention, learning, and memory due to the production of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. Damage in this area results in a decrease in the production of this neurotransmitter, leading to cognitive deficits. Consequently, the degeneration of this region is closely linked to the severity of memory loss and cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s, making it a critical area of focus for understanding its mechanisms and developing targeted treatments.
how to support a loved one with alzheimer’s
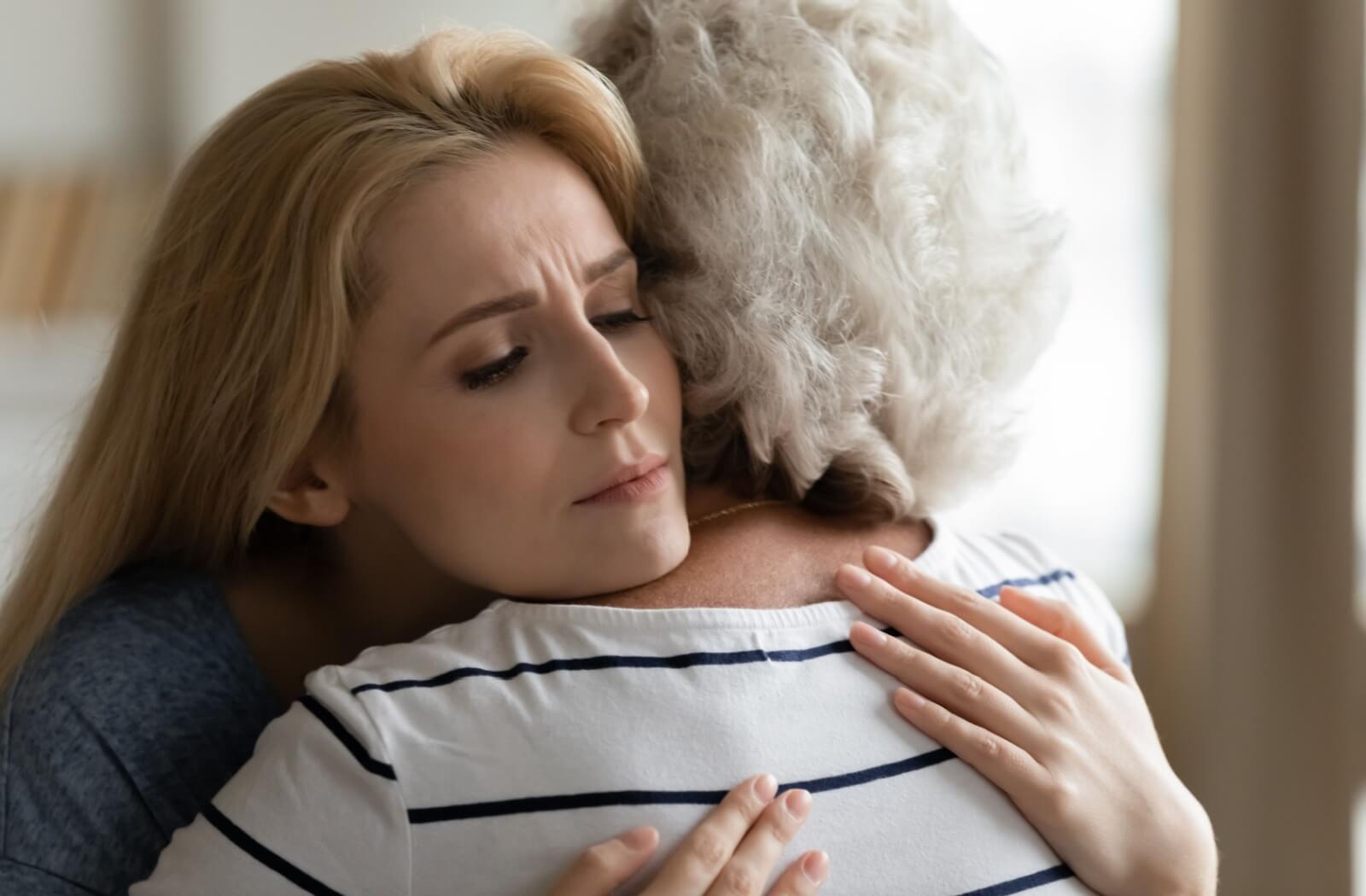

Supporting a loved one with Alzheimer’s involves having empathy, being patient, and being dedicated to working through the difficulties as a team. A supportive environment must be created by instituting a routine that gives them a sense of comfort and consistency but is also adaptable to meet their unique requirements.
Communication is key. Be sure to speak calmly, clearly, and reassuringly, listening and validating their feelings when conversations become difficult. Engaging in activities that can stimulate their mind and body tailored to their abilities is also crucial. Safety is also crucial, so consider home modifications to prevent accidents or falls.
Remember, caring for someone with Alzheimer’s is a journey that requires compassion, resilience, and love, offering moments of joy and connection despite the challenges.
how to support a loved one with alzheimer’s
Understanding the brain regions impacted by Alzheimer’s disease aids in our comprehension of the symptoms faced by those who have the disease and their loved ones. This information is essential for family members and caregivers to provide more compassionate and efficient support. At Silver Comet Village, we’re dedicated to giving older adults with Alzheimer’s specialized care that meets their needs and improves their quality of life. To learn more about our services and experience, book a visit with us today.